Once a tumour is
diagnosed in anyone body, there is a quick response from the patient, which is
mentally, emotionally and physically alarming. One can be terrorised when the
term tumour is posed before them especially when we encounter benign or
malignant tumour. The two differ in many ways, however, most importantly their
difference is being non cancerous and cancerous respectively. Understanding the
way these tumours grow would recognize the prognosis of different steps would
need in order to correct the imbalance that causes the same and the amount of
impact it will have on the future health. Now, let us understand the difference
between the two types of tumours in the following paragraph as under:
Benign Tumour
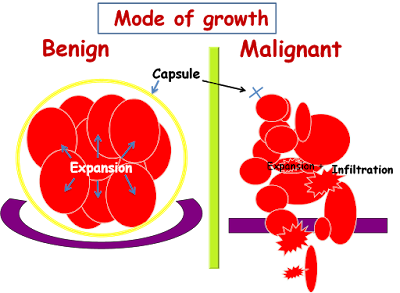
These types of
tumours are often non cancerous in nature. It is very much similar to the
cancer since the growth come along due to the result of abnormal cells. But
unlike any other cancer tumour, it is simply unable to spread the other kinds
of areas of the body and it will not impact to any nearby tissues. It carries
enough which stays at the point of its growth. However, in terms of fatality,
these tumours are not lethal or unhealthy though the location of this tumour
may cause problems. The mass of the tumour would add pressure over the primary nerve
along with the main artery, which compresses the brain content and hence even
the benign tumour can be problematic. Some of the probable causes to this
tumour include traumatic injury over the tumour location along with the chronic
inflammation, which gives undetected infection.
Benign Tumours and its Common Types
The benign
tumours are found with different types, however, the following are the common
types:
- Adenomas (covers the organs and glands)
- Meningiomas (covers the brain and spinal cord)
- Fibromas/ fibroids (mostly seen over woman’s uterus)
- Papillomas (seen over the skin, cervix, breast & mucus membranes)
- Lipomas (are the fat cells)
- Nevi or moles
- Myomas or the muscle tissues
- Hemangiomas or the blood vessels and skin
- Neuromas or the nerves
- Osteochondromas or bones
The treatment
for these types of tumours would depend upon the location, symptoms and causes
of the same. However, when you compare the treatment of benign tumour with the
malignant tumour, the former is simple to treat, while its prognosis is often
favourable.
Malignant Tumour
It is a
cancerous tumour as the term malignant comes from a Latin word meaning badly
born. These types of tumours have the capability to multiply uncontrollably and
thus spread at various organs within your body. These are formed due to the
abnormal called, which are very much unstable and passes through the blood
stream, lymphatic system and circulatory system. These do not carry any
adhesion molecules in order to anchor the original growth of the location wherein
the benign tumours are present. The causes to the same can vary from one place
to other. Some of the factors that are responsible for these tumours include
obesity, alcoholism, smoking, environment pollution, poor diet, household
toxins, etc.
Malignant Tumours and its Common Types
There are two
most common types of malignant tumours present, which are as under:
- Sarcoma (a fat seen over tendon and cartilage)
- Carcinomas (found over the organs like prostate, lung, cervix, etc)
Read more about :


1 comments:
Hematological tests require a lot of mixing and agitation, which is difficult to do manually and hence, automatic mixing and agitation can be conducted with the help of these instruments. Hematology equipment also includes software that helps make data entry easy.
Need more information - http://bit.ly/1O8c6MZ
Post a Comment